Is Microsoft Azure the best place for high-scale workloads?
Azure offers various workload-specific services and tools to ensure high availability, performance, and resilience of workloads.
Written by Natasha Luzinda
There is an almost limitless choice of storage solutions available with Microsoft Azure and it works particularly well with the high workloads of modern applications.
But before we start, we need to have a conversation around throughput and IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) in terms of storage:
- IOPS refers to the number of requests – whether they’re read, write, sequential or random -an application sends to storage disks.
- Throughput measures how much data is transferred to and from the storage device.
- Both are measured per second and throughput is normally measured in MB/s.
So how can Azure handle both? Your ideal solution will be able to manage high volumes of data and requests in a reliable and secure manner with no issues. You also want this to be done while maintaining a low latency.
Storage-optimised virtual machines (VMs)
As outlined by xTEN, an Ekco company, in their informative Cloudbusting series, it’s important to select the right VM family and size for your needs. VMs that are optimised for storage can be an excellent choice for several use cases, including big data, data warehousing, and large transactional databases. They work well because they perform well when dealing with elevated levels of input/output and throughput.
Ultra Disks
Ultra disks are the best performing disk storage option. Disk sizes can vary from anything between 4GB and 64TB. Size matters because the larger the size of the disk, the more IOPS and throughput it can handle. Some of the capacities are outlined below:
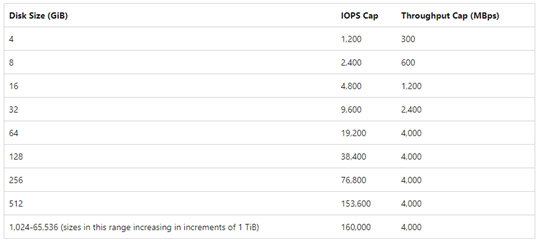
There are, however, some limitations to ultra disks. They don’t support disk encryption and are not (currently) supported by Azure Backup. Should this mean they’re not a viable option for you, Azure has an alternative: Premium solid state drive (SSDs).
Premium SSDs
Premium SSDs provide high performance with cost efficiency in mind. Like ultra disks, they come in assorted sizes. They are an excellent choice for SQL servers, Mongo DB, big data, and analytics. In terms of capacity and performance, Premium SSDs range from P1 (4 GB) to P80 (32 TB), with maximum of 20,000 IOPS and 900MB/s of throughput.
More about our Managed SQL Services
Disk Striping
Disk striping is bringing multiple disks together to behave as one large disk. This can overcome performance limitations with one singular disk, thus giving you an increase to your I/O and throughput limits.
Why disk striping? It can be a more cost-effective solution than simply upgrading the Azure disk tier or VM. For example, you can combine two 2TB data disks (P40) to make one 4TB volume, resulting in 15,000 IOPS and 500 MB/s
So how do you do it? You use ‘storage spaces’ to stripe disks together on Windows machines. This makes the process more user friendly. It allows you to stripe multiple drives on your VM using PowerShell or the Graphical User Interface (GUI). And should you need additional storage, adding another drive to your storage pool is straightforward.
Azure Storage
No matter what data scenario you are faced with, Azure Storage has a service that will fit into your infrastructure to meet your requirements. Azure offers four services that take availability, security, accessibility, and scalability into consideration. Each option allows for the storage of substantial amounts of data within the cloud. The limits are linked to the storage account, which has a maximum capacity of 550TB. But you are not limited to one storage account. You have the option to use up to 250 storage accounts, per region and per subscription with Azure Storage. This should be more than enough for all use cases.
Azure Storage’s four services are:
Azure Blob – For unstructured data. It’s a highly scalable solution for scenarios such as storing for backup and restore, disaster recovery, distributed access, archiving or storing data for analysis to name just a few.
Azure Files – A fully managed cloud file share. Use cases include sharing data between applications, lift-and-shift. A perfect replacement for a file server.
Azure Queues – The solution for storing large numbers of message. These can build up when messages get exchanged between components on-premises and in the cloud and some queues can contain millions of messages.
Azure Tables – The solution for NoSQL datastore in the cloud. Stores large volumes of structured, non-relational data. Can contain unlimited number of tables within a storage account. Capacity is capped at the maximum storage for the storage account.
Whatever your specific requirement, Azure certainly has a solution to handle your storage workload. The key is to understand the best fit for you and how to optimise it for your business.
If you’d like more information or support around this topic, we’re happy to consult with you on your specific needs. Chat to our specialists

Question?
Our specialists have the answer
